Scientific Program
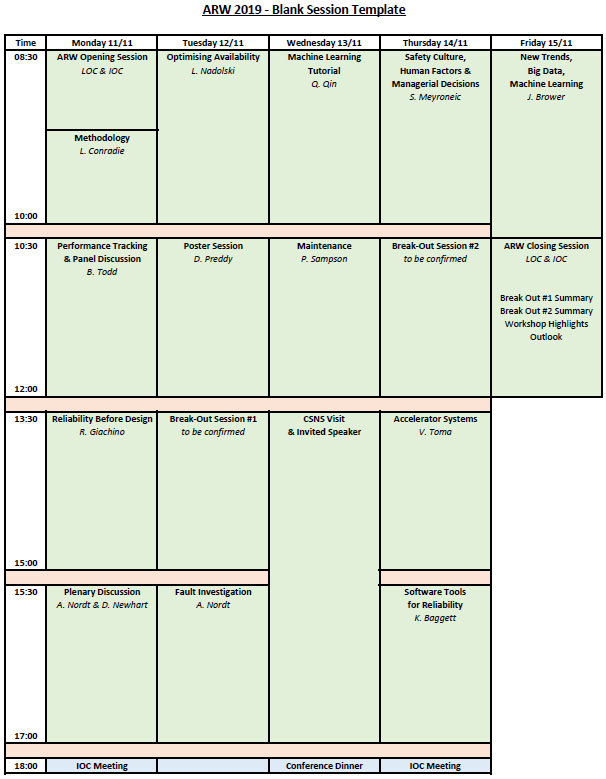
1. ARW Opening Session
Welcome & introduction to accelerator reliability workshop.
2. Methodology
Session Chair: L. Conradie
Abstract: We all have methods, rules and hypotheses in place to drive safety, maintenance, installation, construction, etc., but what methods, rules and hypotheses are in place to drive reliability and availability? What is providing the direction to ensure higher performance? Inclusion of all types of accelerator platforms.
3. Performance Tracking & Panel Discussion
Session Chair: B. Todd
Abstract: Performance as related to "reliability and availability", not "beam" performance. All machines consist of technical equipment and operators who exploit this equipment for their final users. Links between these are crucial to achieve high availability, as higher availability comes from a higher MTBF and a shorter MTTR. A lower MTTR comes by effectively managing repairs, A higher MTBF comes in part form designing more reliable equipment, based on operational needs and past experience.
4. Reliability Before Design
Session Chair: R. Giachino
Abstract: Reliability and availability requirements are taken in consideration long before the design will start. Knowing how to calculate reliability is important, but knowing how to achieve reliability is equally, if not more, important. Reliability practices must begin early in the design process and must be well integrated into the overall product development cycle.
5. Plenary Discussion
Session Chairs: A. Nordt, D. Newhart
Abstract: Open group discussion.
6. Optimising Availability
Session Chair: L. Nadolski
Abstract: Even the most reliable system will not be productive without availability. How are your reliable systems working in concert to ensure the best availability?
7. Poster Session
Session Chair: D. Preddy
Poster presentation requirements, and possible topics.
8. Break-Out Session #1
Session Chairs: TBD (chair and co-chair for each of the two parallel discussions)
Abstract: Two/More parallels session topics TBD from Plenary Discussion
9. Fault Investigation
Session Chair: A. Nordt
Abstract: The session aims for presentations of different methods and tools used to systematically (and automatically) examine fault conditions: from detection, through analysis and on to recovery, e.g. resuming beam operation or patient treatment. The presentations can be interactive by presenting the tools "in action".
10. Machine Learning Tutorial
Session Chair: Q. Qin
Abstract: Machine Learning (ML) is a subfield of artificial intelligence. The term applies broadly to a collection of computational algorithms and techniques that train data-driven models to perform some task, such as classification, regression or anomaly detection, in lieu of statistical approaches. Although ML has already been applied in some instances to particle accelerators, the recent advances (e.g. deep learning) and heightened interest in the community indicate that it will be an increasingly valuable tool to meet new demands for beam energy, brightness and stability. The intent of this tutorial is to provide an introduction to how problems in accelerator science and operation (in particular accelerator reliability) can be tackled using ML-based techniques, and how these can provide a significant benefit over a standard approach. In addition to the tutorial, a related talk exploring the application of ML techniques will be presented.
11. Maintenance
Session Chair: P. Sampson
Abstract: Predictive, preventive and corrective maintenance criteria to improve reliability and maximize maintenance effectiveness. Strategy for maintenance periods; number per year, duration, commissioning periods. Is there a different philosophy depending on machine type; Therapy, Light Sources, Spallation Sources, etc.
12. Safety Culture, Human Factors and Managerial Decisions-was "How to recover from downtime"
Session Chair: S. Meyroneic
Abstract: Whatever the reasons of a stop and its duration, the recovering contains several kinds of difficulties. Obviously, in the cases of prepared or well-known situations, the natural steps (lock-out, tests, validation etc), often already documented, can be easily managed. What procedures are used, and decision processes in place to manage downtime; prepared, foreseen situations, versus unexpected ones. What kinds of documentation and what hierarchies are in place for making decisions concerning machine availability. How is the safety / availability culture maintained, and fostered in each organisation.
13. Break-Out Session #2
Session Chairs: TBD (chair and co-chair for each of the two parallel discussions)
Abstract: Two parallels session topics TBD from Plenary Discussion
14. Accelerator Systems
Session Chair: V. Toma
Abstract: accelerator systems and subsystems often need to be modified to improve performance, reliability and availability. Upgrades can be done incrementally or all at once. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages.
15. Software Tools for Reliability-was just "software"
Session Chair: K. Baggett
Abstract: Production output, fault tracking, reliability and availability are some of the metrics used to assess facility performance. What software tools are being used at your facility to track and analyse metrics. Are your software tools developed in-house or commercial products? Process examples and live demonstrations are encouraged.
16. New Trends, Big Data, Machine Learning-was"Innovations in Accelerator Automation and Robotics-J. Browerx" and "Big Data and Machine Learning-D. Newhart"
Session Chair: J. Brower
Abstract: Innovation in automation and robotics is a progressive part of increasing productivity in the particle accelerator community. From handling, repetitive tasks to reducing stress and increasing safety for the workforce, we look to see where and how the accelerator industry is utilising this technology including in-house development. Using Big Data analytics to discover useful otherwise hidden patterns to incorporate data-driven decisions for facilities. Applying Machine learning techniques to model, explore and implement your data set.
17. ARW Closing Session
Summaries, highlights and outlook.

